Lau, Corinna
Researcher
Bodø
Education: MSc, PhD
E-mail: Corinna.Lau[at]nordlandssykehuset.no
Focus: Characterizing distinct and crosstalk mechanisms that define the very early cellular-dependent innate immune response upon complement and CD14 activation
Bio
Title: Characterizing distinct and crosstalk mechanisms that define the very early cellular-dependent innate immune response upon complement and CD14 activation.
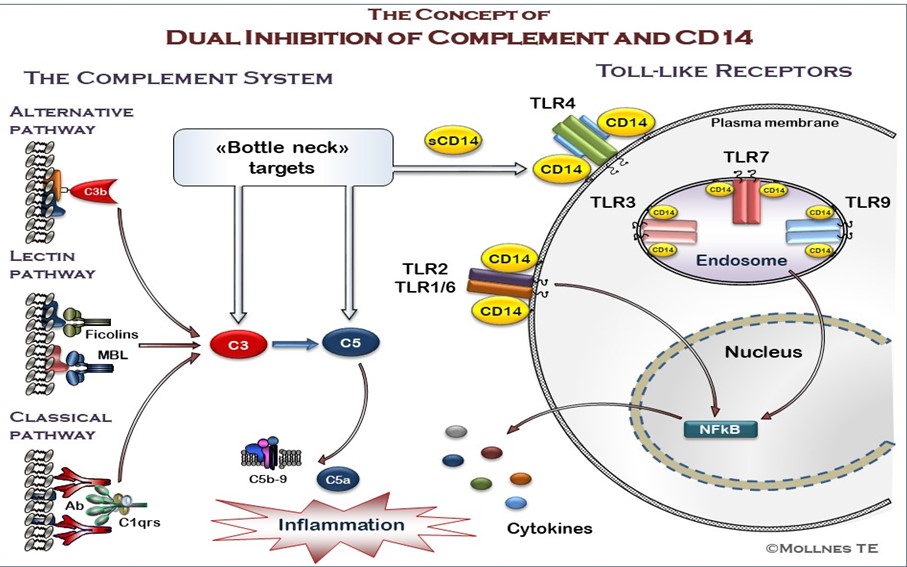
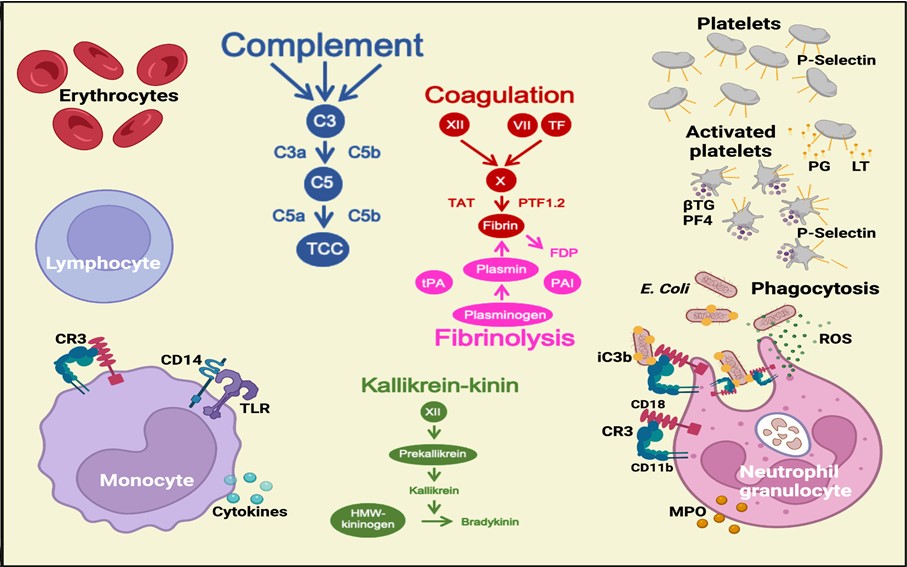
The complement system and Toll-like receptors, with co-receptor CD14, are first line pattern recognition molecules (PRMs) in systemic and local innate immune responses towards danger associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), through both distinct and crosstalk mechanisms. If timed correctly, their simultaneous blockade reduces the inflammatory response immensely, potentially saving the host from life threatening systemic failure like in sepsis or trauma.
The project aims at characterizing differential and synergistic mechanisms that define the very early cellular-dependent innate immune response upon complement and CD14 activation, mainly in bacteria-induced systemic inflammation using an ex vivo whole blood model, with or without pharmacological inhibition of signal transducers and PRMs.
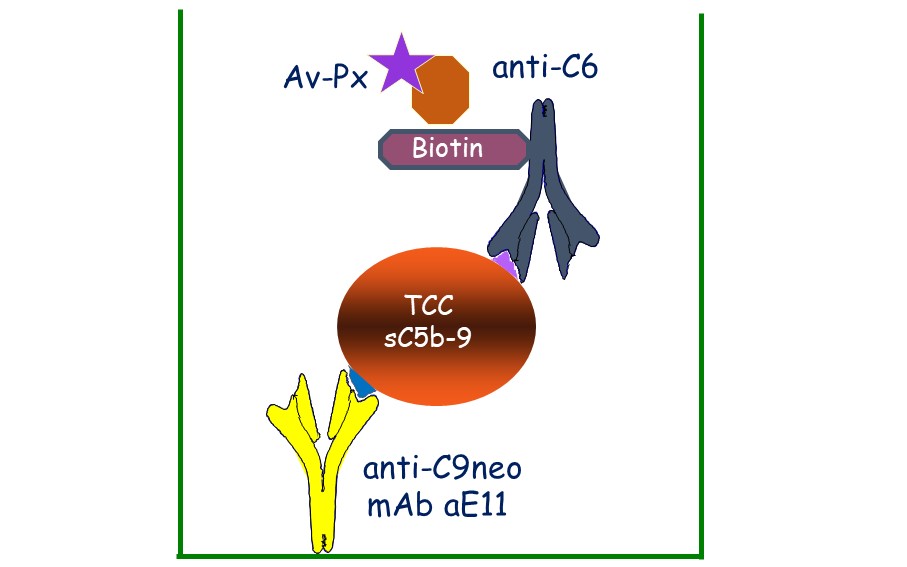
Appropriate downstream analyses are multicolour and intracellular flow cytometry for the evaluation of protein and mRNA expression or posttranslational modification on a single cell level, as well as ELISA and Multiplex immunoassays to detect fluid phase mediators. Furthermore, different magnetic bead-based cell depletion approaches allow for studying cell-type specific contributions to the whole blood response, and also enable more complex downstream analyses on more homogenous cell populations.